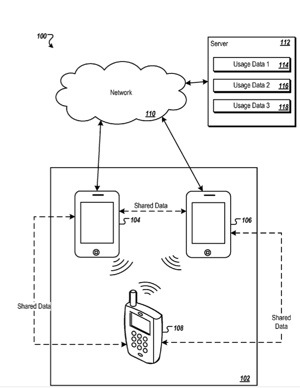
An Apple patent (number 20110142016) at the US Patent & Trademark Office shows that Apple is working on a new social app. The patent is for methods, program products, and systems for ad hoc networking based on content and location are described.
A user of a mobile device can identify another user using another mobile device who is close by, if both users have requested to participate in networking. Common interests and experiences of two or more users located close to each other can be identified from content, including automatically created usage data of the mobile devices. Usage data of a mobile device can be created based on activities performed on the mobile device (e.g., songs downloaded), a trajectory of the mobile device (e.g., places traveled), or other public data available from the mobile device (e.g., pictures shared).
Each of the users can be notified that another user having the common interests and experiences is close by. A means of initiating communication can be provided to the users to facilitate communication between the users. Shuvo Chatterjee is the inventor.
Here’s Apple’s background and summary of the invention: “Social networks are a well known phenomenon, and various electronic systems to support social networking are known. Growing a social network can mean that a person needs to discover like-minded or compatible people who have similar interests or experiences to him or her. Identifying like-minded people, however, often requires a substantial amount of and time and effort because identifying new persons with common interests for friendships is difficult. For example, when two strangers meet, it may take a long and awkward conversation to discover their common interests or experiences.
“Today, various social networking technologies exist to aid the process of connecting people. A typical modern computer-implemented social networking application requires each user to provide some biographical information, and/or identify his or her interests, and in some instances can suggest to the user other users with compatible interests.
“For example, some web sites such as LinkedIn.com or Facebook.com require participants to register as members. Each member can fill out a profile or provide other personal data such as professional interests, career information, interests in music, books, movies, and even information about political or religious beliefs.
“Matching algorithms can then use the profile or data provided to match members with members who are deemed compatible by the algorithms, under the assumption, for example, that matching people’s interests and values can lead to successful new friendships or relationships within the social network. Some mobile device-based applications for identifying common interests require each user to configure the user’s mobile device, including entering the user’s interest, such as the things the user wishes to buy or sell, the kind of people the user wishes to meet, etc., before a social networking opportunity can be found for the user.
“Methods, program products, and systems for ad hoc networking based on content and location are described. A user of a mobile device can identify another user using another mobile device who is close by, if both users have agreed to participate in ad hoc networking based on content and location. Users can be matched based on the users’ common interests and experiences. Common interests and experiences of two or more users located close to each other can be identified from content, including automatically created usage data of the mobile devices.
“Usage data of a mobile device can be created based on activities performed on the mobile device (e.g., songs downloaded), a trajectory of the mobile device (e.g., places traveled), or other public data available from the mobile device (e.g., pictures shared). Each of the users can be notified that another user having the common interests and experiences is close by. A secure means of initiating communication can be provided to the users to facilitate communication between the users.
“Techniques for ad hoc networking based on content and location can be implemented to achieve the following exemplary advantages. Two strangers located closed to each other, both having requested to participate in the ad hoc networking based on content and location, can start a conversation from common interests or experiences identified by the ad hoc networking based on content and location.
“The identified common interests or experiences can be based on actions a user actually performed, rather that what the user says he or she did or liked. People often desire to meet other people for a variety of reasons (e.g., job-seeking, friendship, dating, business, casual conversation, or political debate). Ad hoc networking based on content and location can serve these needs by identifying commonalities between people, without being limited by specialized algorithms (e.g., algorithms tailored for friendship, business relationships, or dating).
“Some other advantages of ad hoc networking based on content and location include the ability to facilitate spontaneous user action. A user at any venue (e.g., in a conference, at a beach, in a bar, on an airplane, etc.) can discover another person near the user, where the other person shares similar experience as the user, if the other person also participates in the ad hoc networking. Ad hoc networking techniques based on content and location can provide “icebreakers” that can encourage spontaneous conversation. The users are not required to pre-define a set of match criteria or to set up meetings based on predefined constraints.”
— Dennis Sellers